DNA Thrombotic Risk Test
Are you at increased risk of serious blood clots?
Blood clots can pose significant health threats. Determine if you’re at a heightened risk for abnormal clotting with the DNA Thrombotic Risk Test.
- Examines variants in the F5, F2, and MTHFR genes.
- 100% private and confidential online results
- Easy at-home mouth swab sample collection
$195.00
Fast, Convenient, Painless
What is Thrombophilia?
Thrombophilia is a medical condition characterized by the blood’s increased propensity to clot. Thrombosis refers to the formation of a blood clot within a vessel, which can obstruct blood flow.
Types of Thrombosis
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): This is a clot that forms in a deep vein, most commonly in the leg. If the clot dislodges and travels to the lungs, it becomes a pulmonary embolus, a potentially life-threatening situation.
- Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis: A rarer and more severe form of clotting, where the clot forms in the dural venous sinuses that drain blood from the brain.
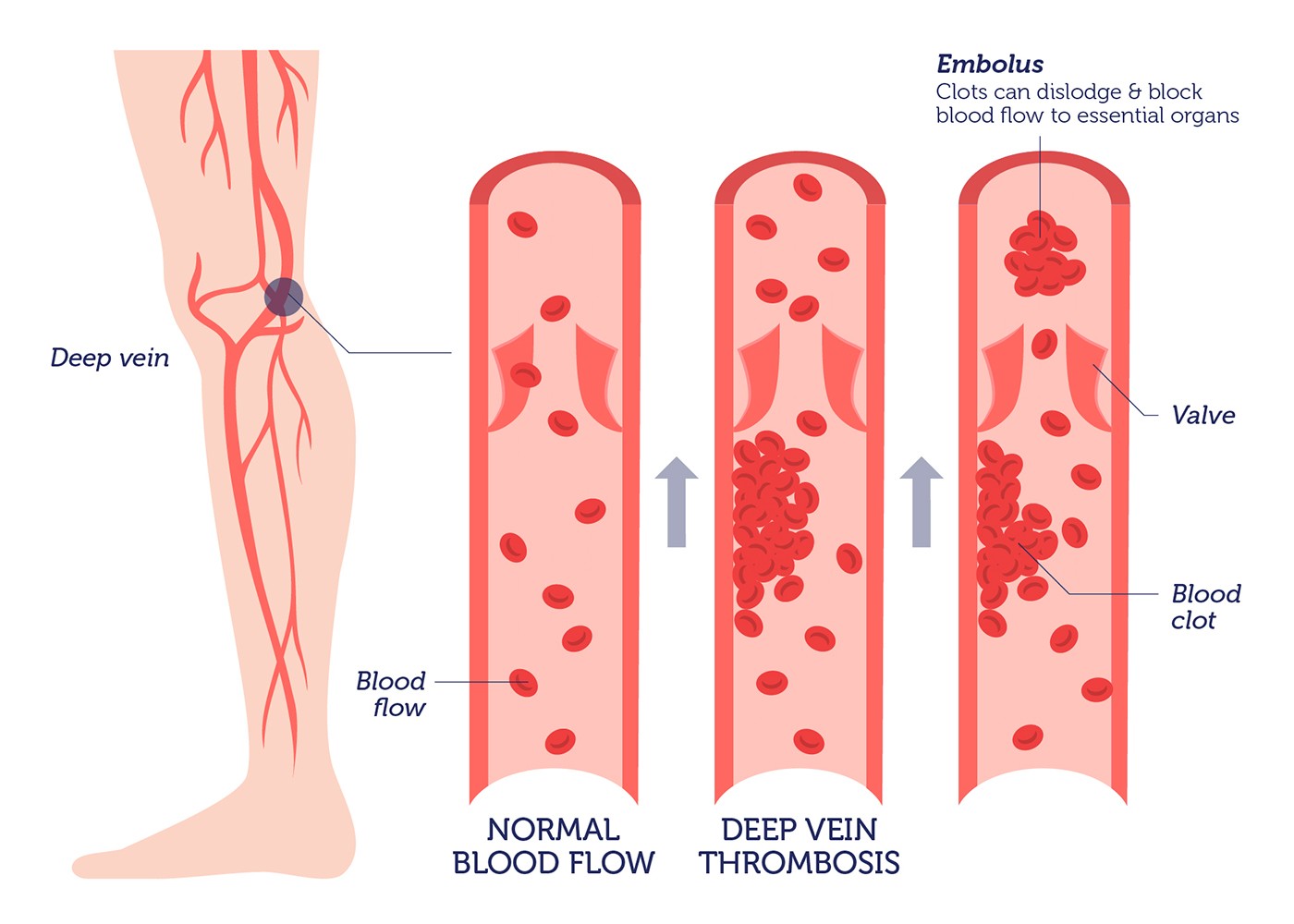
Signs and Symptoms of Thrombophilia
Thrombophilia can manifest in various ways, depending on where a clot forms and its severity. Recognizing these symptoms early can be crucial for timely intervention and treatment. Here are the primary manifestations:
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Pain, swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected area, typically the leg.
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE): Sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, coughing up blood, rapid heartbeat, feeling lightheaded, and rapid breathing.
- Cerebral Venous Thrombosis: Impaired speech, mobility issues, vision problems, and severe headaches.
Risk Factors for Thrombophilia
Several factors can increase an individual’s risk of developing thrombophilia. These range from health conditions and lifestyle choices to genetic predispositions. Being aware of these factors can help in prevention and early detection. Here’s a breakdown:
- Health-Related: Injury, surgery, infections, inflammatory diseases, diabetes, and cancer treatments.
- Lifestyle and Environmental: Sedentary behavior, obesity, and smoking.
- Hormonal Changes: Use of contraceptive pills, hormone replacement therapies, and pregnancy.
- Other Factors: Elevated homocysteine levels due to Vitamin B deficiency, reduced kidney/liver/thyroid function, high blood pressure, certain medications, and excessive coffee consumption.
- Unmodifiable Factors: Age, ethnic background, and inherited genetic mutations.
Variants Tested
This test delves into the genetic variations in three genes that can influence your risk of thrombosis, a condition where blood clots form in blood vessels.
- F5 – the Factor V Leiden mutation (1691G>A)
- F2 – the prothrombin mutation (20210G>A)
- MTHFR – two mutations (677C>T and 1298A>C)
Genetic Inheritance and Its Implications
Each individual inherits two copies of every gene, one from each parent. This means that for each of the genes F5, F2, and MTHFR, you can have:
- Two standard copies (homozygous normal).
- Two mutated copies (homozygous mutant).
- One standard copy and one mutated copy (heterozygous).
Each combination of these genes corresponds to a distinct risk level for thrombophilia.
Thrombotic Risk by Patient Genotype
- F5 (heterozygous 1691G>A) – 3-8x increased thrombosis risk; 2-11x increased miscarriage risk
- F5 (homozygous 1691G>A) – 10-80x increased thrombosis risk; 2-11x increased miscarriage risk
- F2 (heterozygous 20210G>A) – 2-5x increased thrombosis risk; 2-3x increased miscarriage risk
- F2 (homozygous 20210G>A) – >5x increased thrombosis risk; 2-3x increased miscarriage risk
- MTHFR (homozygous 677C>T) – Increased thrombosis risk if folate levels are low
- MTHFR (677C>T and 1298A>C) – Increased thrombosis risk if folate levels are low
How Home DNA Testing Works

Order Test Kit
From relationship tests to health tests, we offer a wide range of DNA tests to fit your needs.

Collect & Ship
Simply collect DNA with our easy-to-use swabs in the comfort of your home.

Receive Results
Access your confidential results online the moment testing is completed. Our team of experts is available for any questions.
Secure & Confidential Online Results